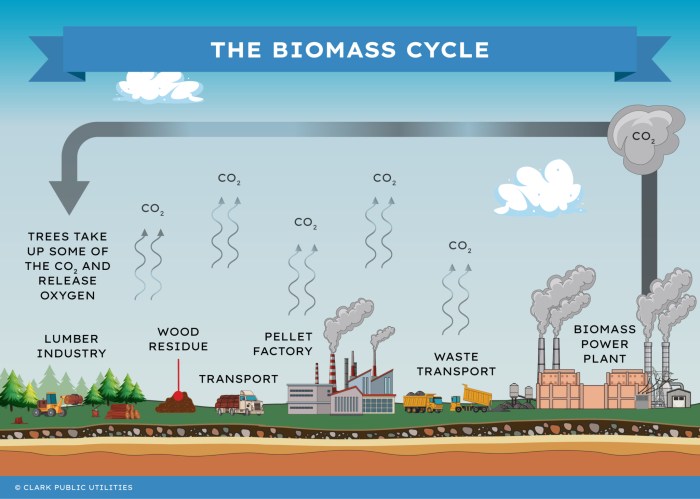
Biomass Energy is a powerhouse in the renewable energy landscape, tapping into organic materials to generate sustainable power. As we become more aware of the environmental impacts of fossil fuels, biomass offers a promising alternative that utilizes waste products from agriculture, forestry, and even municipal sources. This energy source not only contributes to reducing carbon emissions but also promotes a circular economy by turning waste into valuable energy.
From wood and crop residues to animal waste and municipal solid waste, the various types of biomass provide diverse options for energy production. The process involves converting these materials into energy through methods like combustion and anaerobic digestion, making it an essential player in our transition toward a greener future.
Biomass Energy Overview
Biomass energy is a form of renewable energy derived from organic materials, including plants, agricultural waste, and other biological substances. It plays a significant role in the renewable energy sector as it provides a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on non-renewable resources. As a versatile energy source, biomass can be used for electricity generation, heating, and as transportation fuels, contributing to a more sustainable energy future.A variety of biomass sources are utilized for energy production.
These include agricultural residues like crop leftovers, animal waste, wood and forestry products, and dedicated energy crops such as switchgrass and miscanthus. These materials undergo specific processes to be converted into usable energy. The two primary methods for energy conversion are combustion and anaerobic digestion, which involve different techniques and outputs.
Sources of Biomass
Biomass can be sourced from several key categories, each contributing uniquely to energy production.
- Agricultural Residues: Leftover materials from crops, such as straw and husks, which can be burned or processed to release energy.
- Animal Manure: Waste from livestock that can be converted into biogas through anaerobic digestion, providing a renewable energy source.
- Forestry Products: Wood chips and sawdust from timber operations can be used for direct combustion or transformed into pellets for heating.
- Dedicated Energy Crops: Plants specifically grown for energy production, such as switchgrass, which are cultivated for their high biomass yield.
Conversion Processes
The conversion of biomass into energy involves various methods, primarily focused on transforming organic material into heat, electricity, or fuel. Two of the most common processes are combustion and anaerobic digestion.
Combustion involves burning biomass to produce heat, which can be utilized for steam generation or electricity production.
In this process, the biomass is fed into a furnace where it is burned, and the heat generated is captured to produce steam that drives turbines to generate electricity.
Anaerobic digestion is a biological process that breaks down organic matter in the absence of oxygen, producing biogas.
This method is particularly effective for managing waste. As microorganisms decompose the biomass, biogas, primarily composed of methane, is produced. This biogas can be combusted to generate electricity or refined into renewable natural gas for use in heating and transportation.Both processes play a vital role in maximizing the energy potential of biomass while simultaneously addressing waste management and reducing environmental impact.
The versatility of biomass energy sources and conversion methods underscores its importance in the transition towards sustainable energy systems globally.
Types of Biomass

Biomass energy is derived from various organic materials, each with distinct characteristics and advantages. Understanding the different types of biomass not only highlights their roles in energy production but also showcases their potential benefits and limitations. This knowledge is essential for making informed decisions about biomass utilization in energy systems.
Wood Biomass
Wood biomass is one of the most common types of biomass used for energy production. This category includes logs, chips, bark, and sawdust from trees. Wood biomass is characterized by its high energy content and availability, primarily sourced from forestry operations and wood processing industries.
Characteristics
Wood biomass has a high calorific value, typically ranging from 15 to 20 MJ/kg, depending on the species and moisture content. It also provides a solid form of fuel that can be easily transported and stored.
Advantages
Utilizing wood biomass can reduce waste from forestry and logging operations, promote sustainable forest management, and support local economies. Moreover, when sourced sustainably, it can have a lower carbon footprint compared to fossil fuels.
Agricultural Residues
Agricultural residues include by-products from crop production and processing, such as straw, corn stover, and sugarcane bagasse. These materials are often considered waste but have great potential for biomass energy.
Characteristics
Agricultural residues vary in chemical composition and energy content, typically ranging from 10 to 18 MJ/kg. Their fiber content makes them suitable for conversion processes like anaerobic digestion and combustion.
Advantages
Utilizing agricultural residues helps in waste management and can provide farmers with an additional revenue stream. It also contributes to soil health through nutrient recycling.
Municipal Solid Waste
Municipal solid waste (MSW) consists of everyday items discarded by the public, including organic waste, paper, plastics, and metals. This biomass source is increasingly being recognized for its potential in energy generation.
Characteristics
The energy content in MSW can vary significantly, usually between 7 to 14 MJ/kg. It requires sorting and processing to maximize the energy yield effectively.
Advantages
Converting MSW into energy reduces landfill use and associated greenhouse gas emissions. It also encourages recycling and resource recovery, making it a sustainable waste management solution.
Comparative Efficiency and Energy Output
When evaluating the efficiency and energy output of different biomass sources, it’s essential to consider factors such as energy density, conversion technology, and feedstock availability.
Energy Density Comparison
Wood biomass usually has a higher energy density compared to agricultural residues and MSW. This superiority allows for more efficient transportation and processing.
Conversion Technologies
Different biomass types may require specific conversion technologies. For instance, wood can be efficiently converted through combustion and gasification, while agricultural residues might be better suited for anaerobic digestion.
Real-world Examples
In Sweden, wood pellets are a primary source of biomass energy, achieving a high energy output. On the other hand, facilities in the U.S. are increasingly adopting anaerobic digestion of agricultural residues to produce biogas, showcasing the versatility of biomass sources.
Biomass Energy Production Methods
Biomass energy production methods are diverse and each method harnesses organic materials in unique ways. Understanding these methods is essential for optimizing energy production and minimizing environmental impact. The main production methods include direct combustion, gasification, and fermentation, each employing different technologies and processes.
Direct Combustion
Direct combustion is the most straightforward method of biomass energy production, where biomass is burned to produce heat, which can then be converted to electricity. This method is commonly utilized in biomass power plants, where wood pellets, agricultural residues, or dedicated energy crops are used as fuel. The technology involved typically includes:
Boilers
These are used to burn biomass at high temperatures, producing steam.
Turbines
The steam generated drives turbines connected to generators, converting mechanical energy into electricity.
Emission Control Systems
These systems mitigate pollutants produced during combustion, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.The efficiency of direct combustion varies but can reach around 20-30% for electricity generation.
Gasification
Gasification converts biomass into a synthetic gas or syngas, which can be used for heating, electricity generation, or as a fuel for vehicles. This method involves heating biomass at high temperatures with limited oxygen, leading to a chemical reaction that transforms the biomass into gas. Key technologies used in gasification include:
Gasifiers
Equipment designed to facilitate the gasification process. They come in different types, such as fixed bed, fluidized bed, and entrained flow gasifiers.
Syngas Clean-up Systems
These systems remove tar, particulates, and other impurities from syngas to improve quality and usability.
Combined Heat and Power (CHP) Systems
These systems maximize energy recovery by using both heat and electricity from the produced syngas.Gasification can achieve efficiencies of 60-80% depending on the system used.
Fermentation
Fermentation is a biological process that converts organic materials, particularly carbohydrates, into biofuels like ethanol. This method is extensively used in producing bioethanol from crops such as corn and sugarcane. The technologies involved in fermentation include:
Fermenters
Large vessels where microorganisms, typically yeast, break down sugars into ethanol and carbon dioxide.
Distillation Units
These units separate ethanol from the fermentation mixture to produce a concentrated biofuel.
Biomass Pretreatment Technologies
These processes enhance the digestibility of raw biomass, making it easier for microorganisms to ferment sugars, leading to higher yields of ethanol.Ethanol production through fermentation can achieve efficiencies of about 40-60%.
Comparison of Biomass Energy Production Methods
Understanding the efficiency and environmental impact of each biomass energy production method is crucial for selecting the appropriate technology. The following table summarizes the key characteristics:
| Production Method | Efficiency (%) | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Combustion | 20-30 | Higher emissions of CO2 and particulates; needs emission controls |
| Gasification | 60-80 | Lower emissions than combustion; cleaner syngas |
| Fermentation | 40-60 | Lower greenhouse gas emissions; land use concerns for feedstocks |
“The choice of biomass energy production method can significantly influence both efficiency and environmental impacts, making informed decisions paramount for sustainable energy development.”
Environmental Impact of Biomass Energy
The environmental impact of biomass energy is a multifaceted issue that encompasses both benefits and potential drawbacks. Biomass energy has been promoted as a clean and renewable alternative to fossil fuels, which can play an essential role in mitigating climate change. However, it is crucial to analyze not only the positives but also the potential adverse effects on ecosystems and air quality.Biomass energy is often touted for its environmental advantages, primarily its carbon neutrality.
When biomass is burned for energy, it releases carbon dioxide (CO2) that was previously absorbed by the plants during their growth. This cyclical process theoretically makes biomass a neutral contributor to overall greenhouse gas emissions. However, the extent of this neutrality can vary based on how biomass is sourced and managed.
Environmental Benefits of Biomass Energy
Utilizing biomass for energy comes with several significant environmental benefits, including:
- Carbon Neutrality: The combustion of biomass is considered carbon neutral, as it releases CO2 that plants absorbed during their lifecycle, thus not increasing the total atmospheric CO2 levels.
- Waste Reduction: Biomass energy can reduce waste by utilizing agricultural residues, forestry byproducts, and municipal organic waste, diverting these materials from landfills.
- Renewable Resource: Biomass is renewable, as it can be continually replenished through sustainable agricultural and forestry practices.
Negative Impacts of Biomass Energy Production
Despite its benefits, biomass energy production can negatively impact ecosystems and air quality. These issues can arise from improper sourcing and production methods, including:
- Ecosystem Disruption: Large-scale biomass harvesting can lead to habitat destruction, loss of biodiversity, and soil erosion, particularly when forests are cleared for energy crops.
- Air Pollution: Burning biomass can release particulate matter, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and other pollutants, affecting air quality and human health.
- Water Usage: Intensive biomass production may require significant water resources, which can lead to depletion of local water supplies and affect surrounding ecosystems.
Sustainable Practices to Mitigate Environmental Effects
To mitigate the adverse environmental effects associated with biomass energy, implementing sustainable practices is essential. These practices can include:
- Sustainable Sourcing: Ensuring biomass is sourced from certified sustainable forests or agricultural practices can help maintain biodiversity and ecosystem health.
- Efficient Technologies: Employing advanced technologies for biomass conversion can improve energy efficiency and reduce emissions during combustion.
- Agroforestry: Integrating biomass production with agricultural practices can enhance land productivity while protecting soil and water resources.
Economic Aspects of Biomass Energy
The economic aspects of biomass energy play a critical role in determining its viability and market potential. As nations seek sustainable energy solutions, analyzing the costs, benefits, and market opportunities associated with biomass becomes essential. This section delves into the economic viability of biomass energy, highlights successful projects, and discusses the impact of government policies.
Economic Viability of Biomass Energy Production
Biomass energy production presents an opportunity for economic growth while contributing to environmental sustainability. The economic viability hinges on several factors including feedstock availability, production technology, and market demand.
Cost of Production
The cost of producing biomass energy can vary significantly based on the source of biomass (e.g., agricultural residues, forestry waste) and the technology used for energy conversion. Innovations in technology have reduced costs and improved efficiency, making biomass a more competitive energy source.
Market Demand
As the global shift towards renewable energy intensifies, the demand for biomass energy is expected to rise. Industries seeking to reduce carbon footprints are increasingly looking towards biomass as a viable option for energy production.
Successful Biomass Energy Projects
Several biomass energy projects around the world have demonstrated successful economic outcomes. These projects serve as models for future investments and illustrate the potential of biomass energy.
Drax Power Station (UK)
One of the largest biomass power plants globally, Drax has converted a significant portion of its coal generation capacity to biomass. This shift has not only reduced emissions but has also proven economically beneficial, with reports of increased profitability due to government incentives and a growing market for renewable energy.
Biosolids to Energy Program (California, USA)
This program converts sewage sludge into energy through anaerobic digestion. The initiative has reduced waste disposal costs while generating renewable energy and creating jobs, showcasing a successful integration of waste management and energy production.
Government Policies and Incentives
Government policies and incentives play a pivotal role in promoting the growth of biomass energy. These policies can significantly influence investment decisions and the overall market landscape.
Renewable Energy Standards
Many regions have implemented renewable energy standards that require utilities to obtain a certain percentage of their energy from renewable sources, including biomass. This creates a built-in market for biomass energy.
Tax Incentives and Grants
Governments often provide tax breaks and grants to encourage the establishment of biomass production facilities. For instance, the U.S. federal government offers investment tax credits for biomass energy projects, making them more appealing to investors.
Research and Development Funding
Investing in R&D for biomass technologies is crucial for innovation. National and local governments are increasingly funding research initiatives aimed at improving the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of biomass energy production.
“Government support is essential for harnessing the full potential of biomass energy, driving innovation, and ensuring economic competitiveness.”
Future of Biomass Energy

The future of biomass energy is promising, with advancements in technology and an increasing commitment to sustainable practices. As global energy needs rise and environmental concerns escalate, biomass energy is positioned to play a significant role in the energy transition. Innovations in biomass utilization and production methods are expected to enhance efficiency and reduce emissions, making it a crucial part of the renewable energy landscape.Challenges exist within the biomass sector, such as competition for land, feedstock supply chain issues, and concerns over emissions from combustion processes.
Overcoming these hurdles will require innovative solutions and a shift towards integrated biomass systems. The industry’s future will also depend on strong policy support and public acceptance of biomass energy.
Challenges and Solutions in Biomass Energy
The biomass energy sector faces several challenges that need to be addressed to ensure its growth and sustainability. Key challenges include:
- Competition for Feedstock: Biomass sources, like agricultural residues, can compete with food production. A balanced approach is essential to avoid disrupting food supply chains.
- Supply Chain Logistics: Efficient collection, transportation, and processing of biomass are necessary to minimize costs and maximize output. Innovations in logistics can improve efficiency.
- Emissions Management: While biomass is considered renewable, combustion can produce greenhouse gases. Technologies such as carbon capture and storage (CCS) can mitigate these impacts.
- Public Perception: Addressing misconceptions about biomass and its environmental impact is crucial. Educational campaigns can help improve public understanding.
- Regulatory Frameworks: Developing supportive policies and incentives can encourage investment in biomass technologies and projects.
Potential solutions to address these challenges include investing in advanced conversion technologies, enhancing research for biomass feedstock production, and developing clear policies that promote sustainable biomass use.
Innovative Biomass Energy Projects Worldwide
Several groundbreaking biomass energy projects are currently under development globally, showcasing innovative approaches to biomass utilization. These projects are designed to enhance energy efficiency, reduce waste, and promote sustainability. Here are some notable examples:
- Bioenergy with Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS) in the UK: This project aims to capture and store carbon emissions from biomass energy production, effectively making it a carbon-negative energy source.
- Advanced Biofuels from Algae in the USA: Research initiatives focus on converting algae into biofuels, leveraging its rapid growth and high oil content to create sustainable energy solutions.
- Integrated Biomass Gasification in Sweden: This project combines gasification technology with biomass to produce synthetic fuels and chemicals, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- Waste-to-Energy Plants in Japan: Designed to convert municipal solid waste into energy, these plants help manage waste while producing electricity and heat for local communities.
- Agroforestry Biomass Systems in Brazil: These systems integrate food production with biomass energy by using crop residues and tree biomass to generate energy sustainably.
Case Studies in Biomass Energy
Biomass energy has manifested its potential through various successful initiatives worldwide, showcasing its viability as a sustainable energy source. This section delves into notable case studies that highlight the efficacy of biomass energy solutions, along with valuable lessons learned that can guide future projects.
Notable Case Studies
Several successful biomass energy initiatives provide insights into operational efficiency and sustainability. These case studies illustrate how diverse approaches can lead to significant energy production and community benefits.
“Successful biomass projects demonstrate that local resources can effectively contribute to energy needs while supporting economic growth.”
- U.S. Green Energy (Florida, USA): This project involved converting agricultural waste into energy, generating over 10 MW of electricity. The initiative not only produced renewable energy but also improved local waste management practices.
- Göteborg Energi (Sweden): Utilizing wood chips and other organic materials, this initiative powers a district heating system, supplying heat to thousands of homes. The project has significantly reduced carbon emissions, setting a benchmark for urban biomass energy applications.
- Biomass Energy Centre (United Kingdom): This center focuses on advancing biomass technology and practices, showcasing successful conversion processes that have achieved over 90% efficiency in energy generation from organic waste.
- Biogas Facility (Germany): A project converting dairy farm waste into biogas has provided both energy and fertilizer, highlighting the dual benefits of biomass utilization in agriculture.
Lessons Learned from Biomass Case Studies
Analyzing these case studies reveals critical insights that can enhance future biomass energy projects.
“Integrating community engagement and robust supply chains is essential for the sustainability of biomass energy initiatives.”
- Community Engagement: Successful projects often involve local stakeholders in planning and implementation, ensuring support and addressing community needs.
- Supply Chain Development: Establishing a reliable biomass supply chain is crucial for maintaining steady energy production and reducing costs.
- Policy Support: Effective governmental policies and incentives play a significant role in the financial viability and growth of biomass energy projects.
- Technology Integration: Utilizing advanced technologies for biomass conversion improves efficiency and reduces environmental impacts.
Implications for Future Biomass Projects
The analysis of these successful case studies emphasizes the importance of strategic planning and adaptability in the biomass sector.
“Future biomass projects should prioritize sustainability, innovation, and social responsibility to maximize their positive impact.”
- Sustainability Focus: Future initiatives must prioritize environmental sustainability by minimizing waste and emissions through smart resource management.
- Innovation and Research: Ongoing investment in research and development is crucial for optimizing biomass technologies and expanding their applications.
- Collaboration: Building partnerships across sectors, including government, private, and academic institutions, can enhance knowledge sharing and resource allocation.
- Public Awareness: Increasing public understanding of biomass benefits can lead to greater acceptance and support for biomass projects.
Ultimate Conclusion
In summary, Biomass Energy stands at the forefront of renewable solutions, offering both environmental benefits and economic opportunities. As we continue to explore innovative techniques and sustainable practices, the future looks bright for biomass as a key contributor to our energy needs. By investing in research and development, we can overcome challenges and fully harness the potential of biomass for a cleaner planet.
FAQ Insights
What is biomass energy?
Biomass energy is derived from organic materials, such as plants and waste, and is used to generate heat or electricity.
How is biomass energy produced?
Biomass energy is produced through various methods, including combustion, gasification, and anaerobic digestion.
Is biomass energy sustainable?
Yes, biomass energy can be sustainable when sourced responsibly and managed to minimize environmental impact.
What are the benefits of biomass energy?
Benefits include reducing waste, lowering greenhouse gas emissions, and providing a renewable energy source.
Are there any drawbacks to biomass energy?
Potential drawbacks include land use competition, air pollution from combustion, and impacts on ecosystems if not managed properly.





